A Brand New Cryptoeconomy
Global demand of cashless payments continues to rise at such a rate that the end of cash as the
payment of choice is now a stark reality. The number of worldwide cashless transactions was over
430 billion in 2015 whilst the rise of mobile payments is expected to exceed $3.8 trillion by 2020.
As people change the way that they interact with money, we have also seen the introduction of a brand-new form of money, cryptocurrencies. It is less than 10 years since the creation of the Bitcoin,
the world’s first digital currency that in turn built a brand new financial ecosystem called the blockchain. Today there are over 1,000 digital currencies8, known as cryptocurrencies, and that number is growing every day.
The advantages of cryptocurrencies over traditional fiat currencies are numerous and impossible for
fiat currencies to match. Today a transaction between two people in different countries can still take
several days and cost the parties a significant share of the money transferred (the average cross
border transaction fee is 7.45%9) as each party in the chain, of which there are many, requires a small
margin for their efforts. This can now be done in seconds using cryptocurrencies via the blockchain
for practically zero cost and more securely than ever before.
But for many people, even those with a strong interest in new technology and better ways of doing
everyday actions, cryptocurrencies are still perceived as an investment instrument. The single most
important step in moving benefits from the conceptual and into the practical mainstream is to enable
people to use cryptocurrencies in the same way as they can any other currency, and that means enabling instant payments with their Cryptocurrency as if it were cash or money stored in their digital
bank accounts.
Crypterium is building Cryptobank 2.0 for the Cryptocurrency era. People will be able to store, spend, exchange and later borrow practically any Cryptocurrency in the same way as they could any other currency, but in a quicker, cheaper and more secure environment than it is possible in any traditional bank or fiat currency. The Cryptobank will be the decentralized core that interlocks the restricted financial world we live in today and a future Cryptoeconomy with limitless borderless opportunities.
Most of the technology for this financial revolution already exists: Apple Pay, Samsung Pay, Alipay; the world’s biggest banks and payment platforms have already installed more than 42 million contactless payment terminals throughout the world, a number that is growing rapidly.
Crypterium will take full advantage of this global contactless phenomenon, but instead of using it for
traditional payment cards using fiat currencies, we will use it for cryptocurrencies through personal
smartphones. We can skip generations of dedicated development by some of the biggest companies
in the world, and adapt that technology to the Cryptocurrency Era within months, or years, but
definitely, not decades.
We anticipate that soon practically any cryptocurrency can be instantaneously transferred into any
local fiat currency anywhere in the world where cashless payments through contactless payments
terminals are possible and in turn can be spent. This will be done quicker, cheaper and safer than
any fiat currency bank has ever been able to achieve. For the retailer, they are none-the-wiser. As far
as they are concerned, they were paid in their currency of choice.
It is just a small step from cashless Cryptocurrency payments to additional banking services, such
as cross border transactions and eventually Cryptocurrency based loans.
Crypterium is aimed on commence operations by delivering one of the best Cryptocurrency mobile
banking payment application available today. As adoption increases, additional services are intended
to be added.
The team at Crypterium has many years of experience building fintech and mobile payment solutions
including the building and launch of one of Eastern Europe’s most important and award winning
contactless payment platform’s PayQR.
Comparing The Worlds Best Traditional Bank with A New Blockchain Bank
With the advent of any new market changing technology, the old world order often struggles to adapt
to the new world realities. It will be no different for the current banking giants who even today cannot
agree whether or not cryptocurrencies are their future or a passing phase. Whilst they decide, new dedicated blockchain based Cryptobanks will take their place in the Cryptoeconomy.
The following table provides just a few examples of the advantages of a new blockchain bank compared to any leading traditional bank.
It is Crypterium’s strong belief that no single blockchain bank will dominate the new Cryptocurrency
banking sector, but rather that a network of new innovative players will drive the market forward and
that within the next 10 years, roughly the same length of time that Bitcoin has been in existence, the
leading blockchain Cryptobanks will be challenging the leading traditional banks for control over the
Cryptoeconomy.
Mobile Cryptobank
Mobile Contactless Payment
Physical bank branches, plastic payments cards, your personal neighbourhood banker, are all things
of the past. Now everything is digital, mobile and contactless. Crypterium is building a new digital
solution to Cryptocurrency era, that does mostly the same things as the current mobile bank providers, but faster, cheaper, safer using cryptocurrency on the decentralised blockchain.
As soon as a customer downloads the Crypterium mobile banking App customers will be able to start
to make transactions in current VISA, Mastercard or UnionPay infrastructure practically instantly.
Gone are the days when you need to apply for a debit card and wait weeks for it to be delivered.
Customers will be able to instantly pay in certain major cryptocurrency (at least BTC and ETH) or in
ERC20 standard tokens for any product or services at any POS terminals (there are already over 42
million installed throughout the world) that are fitted with NFC (near field communication) via the
Crypterium mobile banking App.
Crypterium uses NFC HCE (host card emulation) protocols to tokenise the data on the virtual payment card and in turn the POS terminal reads the connections as if it were a standard plastic card.
Practically any NFC payment service, such as Apple Pay, Samsung Pay, Google Pay and a host of
other providers, can now be used to pay with cryptocurrencies and as far as the retailer or online store is concerned, they are paid in the currency of their payment order. This capability possibly extends to ATM cash withdrawals and most other standard banking activities.
Today it is practically impossible to pay for your daily coffee, the morning newspaper, or your utility
bill with cryptocurrency. Of course, a cryptocurrency owner could make an exchange of cryptocurrency on one of the exchanges, wait for confirmation that it is completed, then wait for the
transfer of funds to their nominated account and so on. But who in all reality would do that to buy a
coffee? With Crypterium’s mobile banking app that changes instantly. The Crypterium mobile
banking app does all of that for the customer. From any cryptocurrency that are preselected by the
user in Crypterium App, perhaps in different percentages depending on their current trading value,
Crypterium does all the communication and ultimately conversion to and payment in fiat without the
user having to do anything other than bring up their smartphone to the NFC terminal and press go.
Only the exact number of cryptocurrency in the order and ratio prescribed are exchanged to meet the
payment needs.
Crypterium Cryptobank Functionality
Software for IOS, Android or Windows Phone smartphones or tablets with “standard everyday
services”, providing opportunity to use (get and transfer certain cryptocurrencies, including BTC and
ETH), and conduct settlements related to fiat currencies. Examples of such services are:
- Transactions in current infrastructure of trade and services outlets all over the world via international payment system (VISA, Mastercard for example)
- Transactions in infrastructure of trade and services outlets connected to Crypterium or being Crypterium partners’ infrastructure
- Replenishment of personal card or bank account
- International transfers to cryptocurrency accounts or bank accounts, including bank cards, without restrictions (other than those applied for anti-money-laundering purposes)
- Special offers for Crypterium’s users in Crypterium partner shops
This type of functionality is planned to be available for use in December 2017 – January 2018
Crypterium Token - CRPT
Crypterium token CRPT – is the core of all transactions made in Crypterium banking platform. No
payment can be conducted without CRPT, its main goal, regulated by smart-contract, is to stimulate
tokenholders to use Crypterium in their daily life, and to attract new users to Crypterium. The only
issue of CRPT tokens will be during the ICO, which in fact is the pre-sale of Crypterium services usage opportunity. Crypterium in future is planning to list its tokens on cryptocurrency exchanges to
enlarge userbase and fulfil users’ expectations to provide the most comprehensive services.
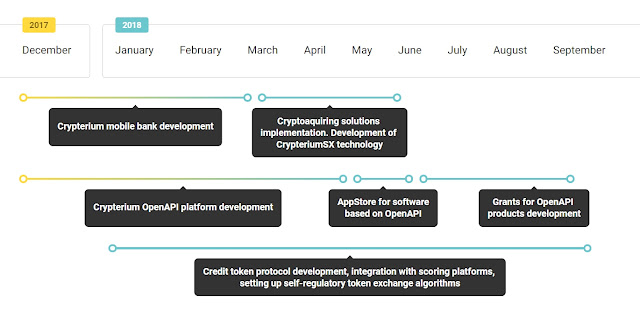
Road map
The achievement of all goals is laid out in this roadmap. We are continually working to meet deadlines, but if delays are required to maintain high standards, the timeline will be be adjusted as necessary.
For More Information :
Website : https://crypterium.io/
Whitepaper : https://crypterium.io/wp/index.html?v=1.01
Twitter : https://twitter.com/crypterium
Telegram : https://t.me/crypterium
Register for ICO : https://tokensale.crypterium.io/
My Bitcointalk Profile : https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=1210304